Los JJ.OO de Tokio podrían cancelarse en las próximas horas
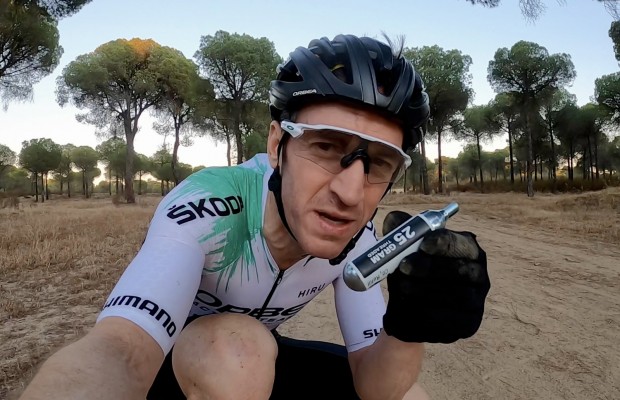
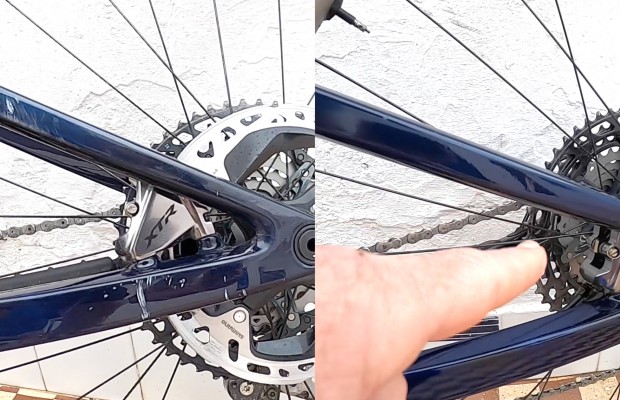


Al detalle la Orbea Oiz OMX de Ibon Zugasti para la Absa Cape Epic 2021


Joyas XXL
Este 2024, las joyas gigantescas son una tendencia de moda global, en la Feria de Abril de Sevilla también. La diseñadora Carmen Marcos, fundadora de CCM Complementos, tiene las claves: "además de los chokers, que son los reyes en Instagram, también vamos a ver pendientes que cuelgan y caen sobre los hombros con cierto aire vintage y creaciones con formas florales. Piezas que además, una vez pasada la feria, pueden utilizarse sin miedo en otros eventos".
Uno de los símbolos de la indumentaria tradicional de flamenca son los volantes y sí, se pueden lucir sin necesidad de enfundarse en un traje. "Por supuesto, para ir a la feria, un vestido midi con volantes o unos pantalones con volantes, funcionan fenomenal. Los volantes llevan varios años saliendo del propio traje de flamenca para dar más personalidad a diseños de fiesta y este 2024, los hemos propuesto en nuestros vestidos de invitada junto a tejidos con estampados propios, bien con lunares o bien con combinaciones de colores vibrantes", explica Carmen Fitz.
Movements and routes through the Darién Gap

The journey through the Darién Gap usually starts in the Colombian ports of Necoclí or Turbo, where local communities offer maritime transportation to the towns of Acandí or Capurganá. Migrants are charged high amounts of money for every section of the trip. After crossing by boat, they must pay again to be allowed to continue through the jungle to the Panamanian side. There are three main paths leading to the government-run reception centres of Lajas Blancas and San Vicente, through the communities of Bajo Chiquito or Canaán Membrillo. The crossing lasts from 5 to 15 days and total costs range from $435 to more than 200,000 per person. There is also a more expensive VIP route, mostly used by Chinese. Migrants and asylum seekers then continue their trip to the Temporary Attention Center for Migrants (CATEM) in Costa Rica, from where, since October, they are directly transferred by bus to the Costa Rica-Nicaragua border. Many, however, run out of money before starting the trek and remain stranded in Turbo and Necoclí, where they are vulnerable to extortion, violence, and human trafficking.